BEST TREATMENT SPECIALIST FOR OVARIAN CYST
Best Ovarian Cyst Treatment in Odisha
WELCOME TO MY GARDEN
ODISHA CENTRE FOR L.I.F.E
(LAPAROSCOPY, INFERTILITY, FIBROIDS & ENDOMETRIOSIS)
Member of ISGE (International Society for Gynecologic Endoscopy)

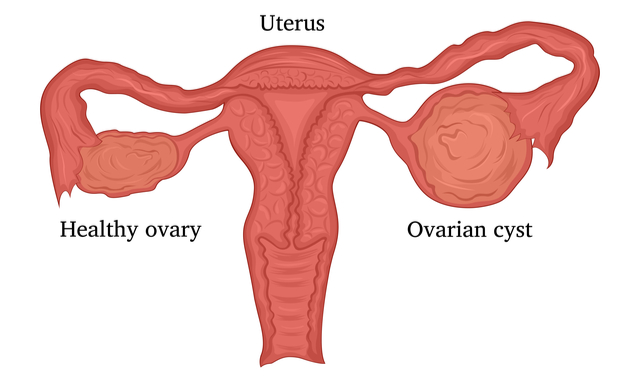
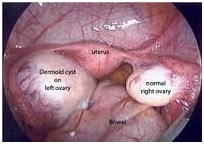
Cysts are fluid-filled sacs that can form in the ovaries. There are several different types of ovarian cysts. The vast majority of ovarian cysts are harmless (benign), most are functional cysts.
FOLLICULAR CYST
the most common type of ovarian cyst. In menstruating women, a follicle containing the ovum (unfertilized egg) will rupture during ovulation. If this does not occur, a follicular cyst of more than 2.5 cm diameter may result.
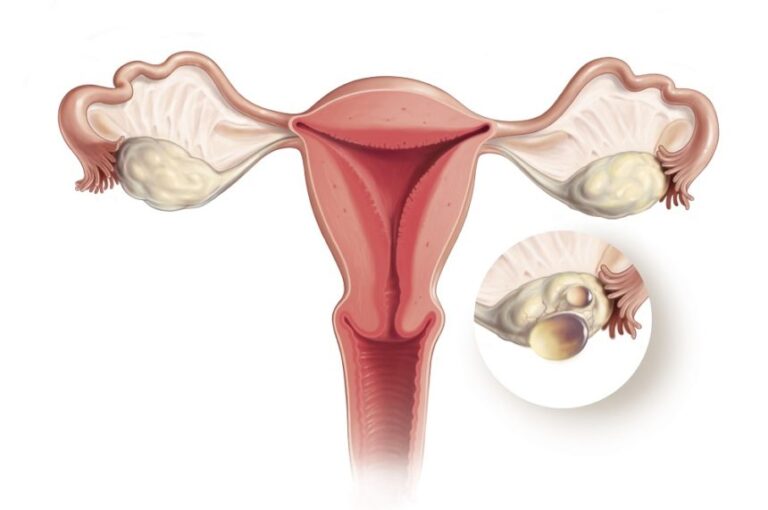
appear after ovulation. The corpus luteum is the remnant of the follicle after the ovum has moved to the fallopian tubes. This normally degrades within 5–9 days. A corpus luteum that is more than 3 cm is defined as CYSTIC.
It is not that all functional cysts require surgery. They can be observed upto 6-7 cm in size without any intervention . They can simply be followed up with a course of oral contraceptive pills( the hormones in the pills may regulate the menstrual cycle, and prevent the formation of follicles that can turn into cysts.(American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, 1999)
- HAEMORRHAGIC ovarian cyst
- POLYCYSTIC OVARIES. In polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), the follicles in which the eggs normally mature fail to open and cysts form.
- ( REFER Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome)
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WmQKW6l1D3g
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OcjAk6MrHB4&t=55s
- CYSTADENOMA (Ovarian serous cystadenoma /Ovarian mucinous cystadenoma):These cysts form out of cells on the surface of the ovary. They are often benign.
- • ENDOMETRIOTIC CYST/CHOCOLATE CYST: In women with endometriosis, tissue from the lining of the uterus grows in other areas of the body. This includes the ovaries. It can be very painful and can affect fertility.
- (REFER Endometriosis Pain Treatment/)
]The stage of pregnancy you are in
Problems that you are experiencing (if any) during your pregnancy
Your health condition and the risks you or your baby may have
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qmrb5442LAU
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iWx_JX3emWA
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tZ4eo5mIADk
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EPGkO_Q_kJ8
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cUE8JoO1QK8
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KO7054eyloY
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sdUNILjWXp0
If tumors are non-cancerous, they are said to be benign. If they are cancerous, they are called malignant.ovarian cysts may cause problems like bleeding and pain ( due to torsion ie twisting of the ovarian pedicle) or may raise concerns of malignancy
1.“All ovarian cysts are not dangerous”.
2.Whenever you have an ovarian cyst detected incidentally on ultrasound, DON’T PANIC. Kindly consult a gynaecologist.
3.If the cyst has altered blood in it with sufficient symptoms of intolerable pain and excessive bleeding per vagina during menses ( chocolate cyst or endometrioma) or the cyst contains teeth, hair etc inside it( dermoid cyst) or the cyst is bilateral, with fluid in the abdomen or has solid component in it, only then it needs urgent attention.
4.ALL OVARIAN CYSTS DO NOT NEED TREATMENT /SURGERY. ONLY SOME DO.
5.Treatment will depend on the type of the ovarian cyst.
- CA 125 ( Normally less than 35 miu/ mL)
- AFP ( ALPHA FOETOPROTEIN)
- LDH ( LACTATE DEHYDROGENASE)
- BETA HCG ( HUMAN CHORIONIC GONADOTROPHIN)
- CEA ( CARCINO EMBRYONIC ANTIGEN)
What are the complaints of people with ovarian cysts
- Abdominal pain. Dull aching pain within the abdomen or pelvis, especially on intercourse.
- Bleeding per vagina .
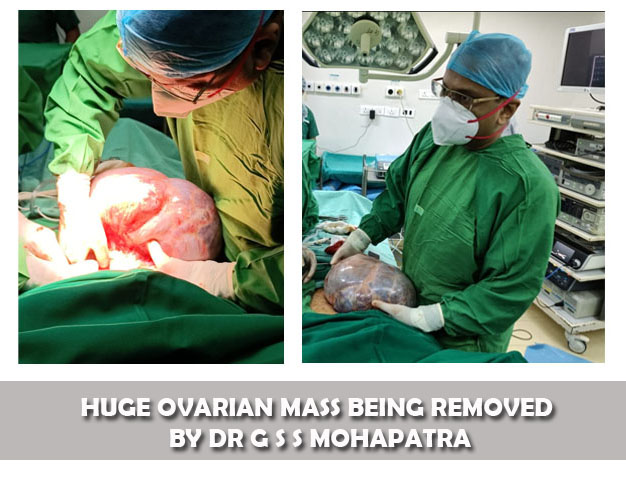
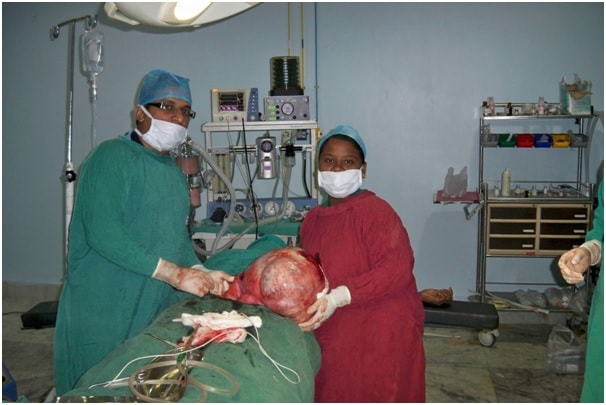
- Fullness, heaviness,of abdomen ESPECIALLY IF THE TUMOUR ASSUMES A BIG/ HUGE SIZE.
- When a cyst ruptures from the ovary, there may be sudden and sharp pain in the lower abdomen on one side.
- Change in frequency or ease of urination (such as inability to fully empty the bladder), or difficulty with bowel movements due to pressure on adjacent pelvic anatomy.
COMMON METHODS OF DIAGNOSI
- USG: to know the side of origin, size, presence of fluid outside the cyst, presence of septa inside the cyst, whether bilateral, whether there is the presence of solid component in it: CT SCAN: all the above information can be better obtained, plus extra information regarding the spread to adjacent and distal organs as well. This will help in designing the roadmap of further treatment and as to how to plan the surgery.
- USG: to know the side of origin, size, presence of fluid outside the cyst, presence of septa inside the cyst, whether bilateral, whether there is the presence of solid component in it:
- CT SCAN: all the above information can be better obtained, plus extra information regarding the spread to adjacent and distal organs as well. This will help in designing the roadmap of further treatment and as to how to plan the surgery.
Persistent complex ovarian cysts
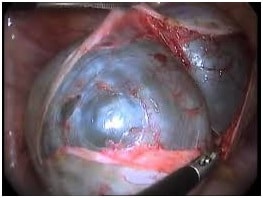
- OVARIAN CYSTECTOMY : In this case only the cyst is removed , preserving the ovary. If the patient is young and we need to preserve the ovaries, then this is the method of choice.
- FEW LINKS ON YOUTUBE FOR OVARIAN CYSTECTOMY BY DR G S S MOHAPATRA:
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g9vmB32I8SM:link showing laparoscopic ovarian cystectomy by DR G S S MOHAPATRA
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0r_JbPbwJvM
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XsHSXxsdifc
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LpDfjaZuY-A
- SALPINGOOPHERECTOMY : Here the tube and ovary is removed if the patient has completed her family,over 40 years of age.
Both the above methods can be done by laparoscopy (minimal invasive surgery) or laparotomy ( cutting open the abdomen ) though laparoscopy is preferred because it can put the patient back in action quickly because of less trauma, smaller incisions ( 0.5 cm), quicker recovery, lesser pain etc
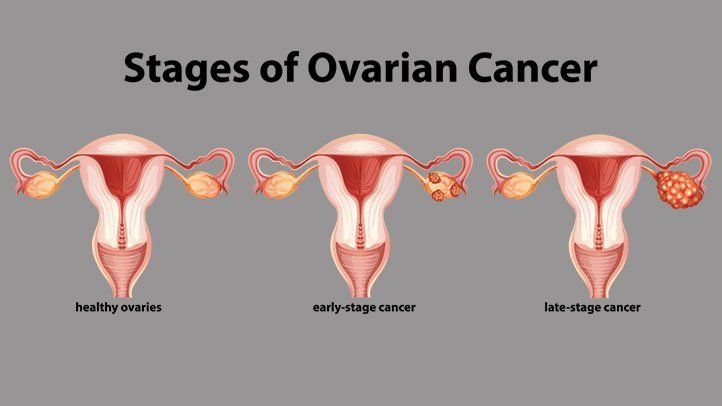
After a woman is diagnosed with ovarian cancer, doctors will try to figure out if it has spread, and if so, how far. This process is called staging. The stage of a cancer describes how much cancer is in the body. It helps determine how serious the cancer is and how best to treat it. Doctors also use a cancer’s stage when talking about survival statistics.
Ovarian cancer stages range from stage I (1) through IV (4). As a rule, the lower the number, the less the cancer has spread. A higher number, such as stage IV, means cancer has spread more. One of the goals of surgery for ovarian cancer is to take tissue samples for diagnosis and staging. To stage the cancer, samples of tissues are taken from different parts of the pelvis and abdomen and examined in the lab.
]The stage of pregnancy you are in
Problems that you are experiencing (if any) during your pregnancy
Your health condition and the risks you or your baby may have
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qmrb5442LAU
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iWx_JX3emWA
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tZ4eo5mIADk
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EPGkO_Q_kJ8
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cUE8JoO1QK8
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KO7054eyloY
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sdUNILjWXp0
If tumors are non-cancerous, they are said to be benign. If they are cancerous, they are called malignant.ovarian cysts may cause problems like bleeding and pain ( due to torsion ie twisting of the ovarian pedicle) or may raise concerns of malignancy
- The extent (size) of the tumor (T): Has the cancer spread outside the ovary or fallopian tube? Has the cancer reached nearby pelvic organs like the uterus or bladder?
- The spread to nearby lymph nodes (N): Has the cancer spread to the lymph nodes in the pelvis or around the aorta (the main artery that runs from the heart down along the back of the abdomen and pelvis)? Also called para-aortic lymph nodes.
- The spread (metastasis) to distant sites (M): Has the cancer spreadto fluid around the lungs (malignant pleural effusion) or to distant organs such as the liver or bones?
Numbers or letters after T, N, and M provide more details about each of these factors. Higher numbers mean the cancer is more advanced. Once a person’s T, N, and M categories have been determined, this information is combined in a process called stage grouping to assign an overall stage.
The staging system uses the pathologic stage (also called the surgical stage). It is determined by examining tissue removed during an operation. This is also known as surgical staging. Sometimes, if surgery is not possible right away, the cancer will be given a clinical stage instead. This is based on the results of a physical exam, biopsy, and imaging tests done before surgery.
Whenever you have an ovarian cyst detected incidentally on ultrasound, DON’T PANIC. Kindly consult a gynaecologist.
3.If the cyst has altered blood in it with sufficient symptoms of intolerable pain and excessive bleeding per vagina during menses ( chocolate cyst or endometrioma) or the cyst contains teeth, hair etc inside it( dermoid cyst) or the cyst is bilateral, with fluid in the abdomen or has solid component in it, only then it needs urgent attention.
4.ALL OVARIAN CYSTS DO NOT NEED TREATMENT /SURGERY. ONLY SOME DO.
5.Treatment will depend on the type of the ovarian cyst.
HOSPITAL
- ANKURA HOSPITAL, BHUBANESWAR
- 9937776329
- NURTURE MOTHER & CHILD clinic GA 190 Gayatri Vihar, Nandankanan Road, Patia Chowk, Next to STYLIVE Furnishings, Jasodha Homes, Bhubaneswar, Odisha – 751024
- 9776822222
drgssmp@gmail.com

